- Escambia County Public Schools
- Biology End of Course Review
- SC.912.L.17.9 Food Webs and Energy Transfer
Science
Page Navigation
- Home
- Elementary Science Curriculum
-
Biology End of Course Review
- Biology EOC Review
- SC.912.N.1.1 Scientific Method
- SC.912.L.18.12 Properties of Water
- SC.912.l.18.9 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
- SC.912.L.18.1 Macromolecules
- SC.912.L.16.17 Mitosis and Meiosis
- SC.912.L.16.3 DNA Replication
- SC.912.L.14.3 Cell Structure
- SC.912.L.14.1 Cell Theory
- SC.912.L.17.20 Human Impact
- SC.912.L.17.9 Food Webs and Energy Transfer
- SC.912.L.17.5 Population Size
- SC.912.L.16.13 Reproductive System
- SC.912.L.16.10 Biotechnology
- SC.912.L.14.52 Immune System
- SC.912.L.14.36 Cardiovascular System
- SC.912.L.14.26 The Brain
- SC.912.L.14.7 Plant Structure
- SC.912.L.16.1 Genetics
- SC.912.L.15.13 Natural Selection
- SC.912.L.15.8 Origin of Life
- SC.912.l.15.6 Classification
- SC.912.L.15.1 Evolution
SC.912.L.17.9 Food Webs and Energy Transfer
ORGANISMS, POPULATIONS AND ECOSYSTEMS
CLASSIFICATION, HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
-
- You need to know how to use a food web to identify producers, consumers, and decomposers.
- You need to know the pathway of energy transfer through trophic levels and the reduction of available energy at successive trophic levels.
- You need to know how matter and energy move through the water and carbon cycles.
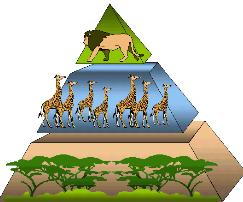
EXAMPLE ONE
-
A team of ecologists observed feeding patterns of several populations in the desert. The energy pyramid shown below depicts the feeding patterns the ecologist observed.
Which of the following best explains the difference in the amount of available energy in the trophic levels of the desert ecosystem?
A. There is less energy available in the producers because their tissues are less dense than those at higher trophic levels.
B. There is more energy available in the second trophic level because less energy is needed for hunting compared to the higher trophic levels.
C. There is more available energy in the birds of prey because they have greater muscle mass for storing energy than organisms in lower trophic levels have.
D. There is less available energy in the fourth trophic level because of the loss of energy through metabolism in each of the lower trophic levels.
EXAMPLE TWO
-
A diagram of a food web is shown below.
Which organism receives the least amount of energy from the producers?
A. Hawk
B. Rabbit
C. Grasshopper
D. Mouse
EXAMPLE THREE
-
The diagram below shows the cycling of nutrients in an ecosystem.
The removal of which of the following groups would cause an immediate decrease in the amount of energy flowing through the system?
A. Producers
B. Consumers
C. Decomposers
D. Inorganic nutrients
EXAMPLE FOUR
-
Complete burning of plant material returns carbon primarily to the
A. herbivores.
B. water.
C. vegetation.
D. atmosphere.
EXAMPLE FIVE
-
Which of these organisms would most likely be found at the top of an energy pyramid?
A. clams - a primary consumer
B. sardines - a primary consumer
C. sharks - a secondary consumer
D. kelp - a primary producer
EXAMPLE SIX
-
The diagram below shows the flow of carbon in a terrestrial ecosystem.
Which will most likely happen if the decomposers are removed from the carbon cycle?
A. The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will increase.
B. The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will decrease.
C. The amount of carbon dioxide used by producers will increase.
D. The amount of carbon dioxide needed by consumers will decrease.
EXAMPLE SEVEN
-
In a process called transpiration, plants get rid of excess water through pores in the leaves called stomata. This excess water is then released into the atmosphere as part of the water cycle. Which of the following terms best describes how the released water enters the atmosphere?
A. condensation
B. precipitation
C. evaporation
D. capillary action
EXAMPLE EIGHT
-
The framework of organic molecules essential to all organisms is composed mainly of carbon atoms. Which processes are involved in the cycling of carbon within an environment?
A. photosynthesis and respiration
B. evaporation and condensation
C. transcription and translation
D. diffusion and transpiration
EXAMPLE NINE
-
Which of the following statements is true about natural systems?
A. Consumers form the bottom levels of both the energy pyramid and the biomass pyramid.
B. Producers are at the bottom level of both the energy pyramid and the biomass pyramid.
C. Producers are at the bottom of the energy pyramid, but at the top of the biomass pyramid.
D. Consumers are at the bottom of the energy pyramid, but at the top of the biomass pyramid.
WATER & CARBON CYCLES
ECOSYSTEM ECOLOGY
TROPHIC LEVELS
ENERGY TRANSFERS IN ECOSYSTEMS
GLOBAL CARBON CYCLE
IN YOUR BOOK
-
General Biology - Sections 13.3-13.6, pgs. 406-419
Honors Biology - Sections 3.2-3.4, pgs. 60-73